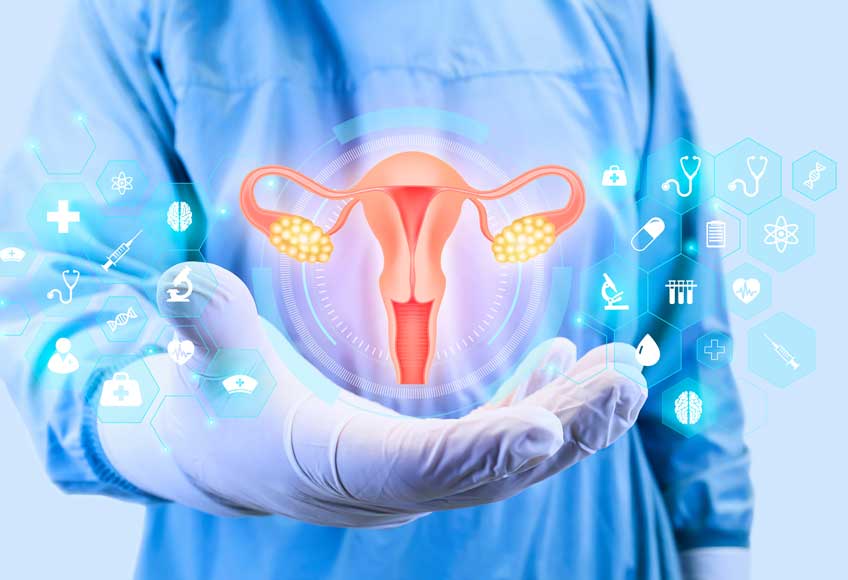
Organ series: ovaries
The health of our organs plays a major role for your well -being and fitness. But do you actually know how every single organ of your body actually works? If you are not studying medicine or are interested in it privately, the answer is usually open to you. Therefore we would like to educate you and bring the human organs closer to you.
In the next few months, new blog posts are waiting for you again and again. We will explain the functions of our organs, the connection with histamine intolerance and much more.
In today's part of our series of organ, everything revolves around the ovaries. Did you know that you can influence your ovaries with your lifestyle?
This plays a major role in the function of the ovaries and also for your fertility. Factors such as stress, smoking and excessive sport can negatively affect the ovaries.
The ovaries are among the most important reproductive organs of the woman, because the egg cells mature in them.
They also control the female monthly cycle and contribute to the development from the girl to a woman.
Tasks and functions of the ovaries
- Provision of fertilizable egg cells
- Production of female sex hormones
A normal menstrual cycle takes about 28 days for the next menstrual bleeding to use, although fluctuations between 25-35 days can also occur. The first half of the cycle (Follicle phase) is due to the effect of the Ability to mature follicles produced estrogen characterized.
The second half of the cycle (Luteal phase) after ovulation by the Progesterone produced yellow bodies determined. Fluctuations in the cycle duration play mainly in the follicular phase, while the luteal phase is largely constant 12-14 days.
In the first cycle phase, primary follicles grow to secondary and finally to Tertiary follicles. Secondary and tertiary follicles mainly produce estrogen. One of the tertiary follicles finally converts in the jumping with Graaf follicles. In the middle of a monthly cycle of the sexual mature wife "jumps" an egg cell from this Graaf follicle. After this ovulation, the egg hikes in the fallopian tube towards the uterus, where it has to hit sperm cells within just a few hours. If the egg has been fertilized, an embryo develops. The emptied Graaf follicle forms to the yellow body and produces the yellow body hormone progesterone.
If fertilization does not occur, the yellow body resigns and sets the progesterone production. The progesterone level in the blood drops, which is why the endometrium can no longer be maintained and is repelled. This is supported by quite painful uterine contractions triggered by prostaglandins. The endometrium now detaches into scraps and is emitted mixed with blood. The menstrual bleeding and thus the first day of the new cycle begin.
After the age of 45, the ovaries gradually interpret their activity- the rain bloodings are becoming increasingly less common and finally failing to stop.
The following hormones are most important for the female cycle:
FSH (follicle stimulating hormone)
- Is released in the first half of the cycle
- Causes the maturation of an egg cell to the Graaf follicle
- The distribution of estrogen from the ovaries
LH (luteinizing hormone)
- Is released in the middle of the cycle
- Together with FSH, ovulation and the conversion of the Graaf follicle into the yellow body
- This yellow body produces the yellow body hormone progesterone
estrogen
- Causes the reconstruction and growth of the uterine mucosa after menstruation
- Affects the maturation of the follicles
- The LH distribution and egg transport
- During puberty, promoting the primary and secondary gender characteristics
- Increases the sex drive (libido)
- Promotes bone maturation
- Improves the absorption of calcium, sodium, and phosphorus
progesterone
- the uterine mucosa prepares for the absorption of the fruit
- Supports the implantation and growth of the embryo in early pregnancy
- Pregnancy effect
- Causes an increased water storage into the tissue
- Prepare milk formation in the breasts
-
Location in the body
The ovaries are among the female genital organs. In technical terms, they are referred to as ovaries. They are located in the lower pool to the right and left between the fallopian tubes and uterus, with which they are connected via the ovarian tapes. The neighboring organs are the worm process, the nerve of the lumbar mesh and the ureter.
-
Mental component
There are strong interactions between the menstrual cycle and the overall organism. Mental factors influence the distribution of FSH and LH through the hypothalamus via the limbic system. This is the reason why in large stressful situations or times of need in many women the menstrual periods fail, can shift greatly or are associated with increased menstrual complaints. And the vice versa also have the sex hormones formed by the ovaries on the other cells of the body. Due to their effect on the CNS, they significantly determine human behavior.
Aggression, depressive mood, fatigue, mood swings, irritability and bad mood can result. These occur particularly strongly in menopause or before menstruation as PMS. Hormones are closely connected to the psyche. However, it can also be mentally due to the lack of children. In this case, it is helpful to pay more attention issues of femininity and mother.
Connection with histamine intolerance
The body reacts to an increased amount of histamine with intolerance reactions. In the ovaries and in the uterus, histamine is produced in the mast cells, endothelial and epithelial cells. Affected women of histamine intolerance therefore often suffer from headaches or dysmenorrhea. The reason for this is that histamine has a contraction -increasing effect. The increase in histamine levels before and during menstruation can therefore be the cause or jointly responsible for cramps and tension during this time. It is also hardly a coincidence that PMS, menstrual complaints, diarrhea and headache are among the typical symptoms of histamine intolerance.
Histamine continues to increase the estradiol synthesis (Estradiol is the most active form of estrogen). Estrogens in turn promote the formation of prostaglandin that causes painful uterine contractions. Histamine can therefore contribute to the increase in dysmenorrhea via the increase in the amount of estrogen. But, conversely, estrogens can also influence the histamine effect: in a test, larger histamine squad on the skin prick test was observed while increasing the estrogen plas mashing. Another study also confirms this assumption: in many women, there was an increased histamine release in the course of the second half of the cycle, which also correlated with the amount of the estradiol level. An estrogen dominance with a low -humiliated progesterone level can therefore increase histamine intolerance. In contrast to estrogen, progesterone has a balancing effect on the histamine balance. If both hormones are in balance, the symptoms can be regulated very well.
The following factors can be the cause of a progesterone deficiency:
- Hormonal contraceptive methods (synthetic progesterone cannot fulfill the function of progesterone)
- Lack of micronutrients (B6, B vitamins, vitamin D, magnesium, zinc, omega-3 fatty acids)
- Overweight
- Permanent stress (the body activates the distribution of cortisol, which is made from progesterone. As a result of the increased consumption, the progesterone level drops and nothing remains for the hormones. An estrog dominance is the result)
- Environmental pollution
Which hormone acts like on the mast cells?
- Mast cell activating: Östrogen, Luteinisierendes Hormon (LH beim Eisprung), follikelstimulierendes Hormon (FSH)
- Mast cell stabilizing: Progesterone, cortisol, melatonin
Symptoms and diseases in histamine intolerance
- Dysmenorrhea (painful menstrual bleeding, whereby the pain can also use the bleeding before the start of the bleeding)
- Cycle -dependent headache
- Cramp -like pain in the lower abdomen
- Itching on the vagina and other parts of the body
- Diarrhea, indigestion, nausea
- Tachycardia
- Cyclical disorders
- Sleep disorders
- Mood fluctuations, fear and panic attacks
- Water retention, breast tension
Advertisement
Example product title
The Histaminikus Red Dragon Zehmer Tea is a slightly bitter herbal tea that Efforts and calming during the period.Women's mantle and chamomile ensure relief for cramp -like symptoms.
Share
Collapsible content
SOURCES
- https://www.aerzteblatt.de/archiv/53958/Die-verschiedenen-Gesichter-der-Histaminintoleranz
- Naturopathic practice today, textbook and Atlas, 3rd edition
- Kalogeromitros D, Katsarou A, Armenaka M, Rigopoulos D, Zapanti M, Stratigos I: Influence of the Menstrual Cycle On Skin-Prick Test Reactions to Histamine, Morphine and Allergen. Clin Exp allergy 1995; 25: 461–6. Medle
- Jonassen F, Granerus G, Wetterqvist H. Histamine Metabolism During the Menstrual Cycle. Acta fruit set gynecol scand. 1976; 55 (4): 297-304. DOI: 10.3109/00016347609158501

From those affected for those affected
We are Thomas and Michaela Zinser, founder of Histaminikus.
Because of the own histamine intolerance of Michaela and our son, we founded Histaminikus. The frustration does not find any suitable histamine food has spurred us to develop low -histamine food.
We would like to give you back a piece of quality of life. Feel free to look around with us.
Kind regards
Thomas and Michaela






